Chemistry - Gas Laws, Thermodynamics
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/47
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
1
New cards
Charasteristics of Gas
Volume, Pressure, Temperature
2
New cards
Units for volume
Litres - L (si unit)
dm^3 - decimeter cubed (convenient and used used in IB)
dm^3 - decimeter cubed (convenient and used used in IB)
3
New cards
Units for temperature
C - degrees celsius
K - kelvin
K - kelvin
4
New cards
Celsius to Kelvin formula
K = C + 273.15
5
New cards
What is the lowest temperature possible in K
0 K: absolute zero
6
New cards
Pressure
The force applied over an area (m^2)
7
New cards
Units for pressure
N/m^2
Pa - pascal
Pa - pascal
8
New cards
Converting pressure units
1\.0 atm = 101325 Pa = 101.325 kPa = 1.01325 bar = 760 torr = 760 mmHg = 14.6959 psi
9
New cards
mmHg
Mercury
10
New cards
Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP)
"Standard" set of conditions
exactly 273 kPa and 100. kPa
exactly 273 kPa and 100. kPa
11
New cards
Standard Ambient Temperature and Pressure (SATP)
exactly 298 K and 100 kPa
12
New cards
Gas Laws
- As pressure increases, volume decreases
- As temperature increases, volume increases
- As temperature decreases, pressure decreases
- As temperature increases, pressure increases
- As temperature increases, volume increases
- As temperature decreases, pressure decreases
- As temperature increases, pressure increases
13
New cards
As pressure increases, volume decreases
P ∝ 1/V
PV = constant
PV = constant
14
New cards
As temperature increases, volume increases
T ∝ V
T/V = constant
T/V = constant
15
New cards
As temperature decreases, pressure decreases
As temperature increases, pressure increases
As temperature increases, pressure increases
P ∝ T
P/T = constant
P/T = constant
16
New cards
Boyle's Law
P1V1=P2V2 @ Constant T
17
New cards
Charlses' law
V1/T1 = V2/T2 @ Constant P
18
New cards
Gay Lussac's Law
P1/T1 = P2/T2 @ Constant V
19
New cards
Combined Gas Laws
P1V1/T1=P2V2/T2 @ constant mols
20
New cards
Units for gas laws
T - always use Kelvin
P, V - units do not matter as long as the units are the same on both sides
P, V - units do not matter as long as the units are the same on both sides
21
New cards
Avogadro's Law
As you add additional gas to a system, the volume of that gas will increase
- temperature and pressure are held constant
n ∝ V
V1/n1 = V2/n2
- temperature and pressure are held constant
n ∝ V
V1/n1 = V2/n2
22
New cards
Ideal Gases + model for the behaviour of gases
I) The volume of gas particles themselves are negligable compared to the volume of the gas
II) There are no attractive forces between the gas particles
II) There are no attractive forces between the gas particles
23
New cards
Ideal Gas Law formula
PV = nRT
24
New cards
R
Ideal gas constant (in units J/k * mol)
Volume in Ideal Gas Law formula must be in m^3, pressure in Pa, and temperature in K
Volume in Ideal Gas Law formula must be in m^3, pressure in Pa, and temperature in K
25
New cards
Thermodynamics
The study of how heat works
energy + temperature relate to each other
energy + temperature relate to each other
26
New cards
1st Law of Thermodynamics - Conservation of Energy
- energy cannot be created or destroyed
- you can only *transfer* energy
- you can only *transfer* energy
27
New cards
Heat
A form of energy
Thermal energy
Thermal energy
28
New cards
Kinetic Energy
the energy of motion
Kinetic Energy - 1/2m(^2)
Kinetic Energy - 1/2m(^2)
29
New cards
m
mass
30
New cards
V
velocity
31
New cards
Temperature (energetics)
a measure of the average kinetic energy
- energy is added to substance -> internal energy goes up -> particles have more kinetic energy -> particles move faster -> higher temperature
- energy is added to substance -> internal energy goes up -> particles have more kinetic energy -> particles move faster -> higher temperature
32
New cards
Boltzmann Distribution

33
New cards
Potential Energy
energy that is stored in a system
34
New cards
Enthalpy (H)
total internal energy of a system
- stored in the bonds
- stored in the bonds
35
New cards
ΔH (delta H)
change in Enthalpy
ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants
ΔH = Hproducts - Hreactants
36
New cards
Endothermic
- total internal energy goes up (increases)
- absorbs heat
- ΔH is positive
- absorbs heat
- ΔH is positive
37
New cards
Exothermic
- total internal energy does down (decreases)
- releases heat
- ΔH is negative
- releases heat
- ΔH is negative
38
New cards
Endothermic reaction
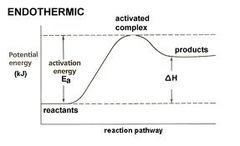
39
New cards
Exothermic reaction

40
New cards
Measuring Enthalpy - Heat Capacity calorimetry
the science or act of measuring changes in state variables of a body for the purpose of deriving the heat transfer associated with changes of its state due, for example, to chemical reactions, physical changes, or phase transitions under specified constraints (google)
41
New cards
Calorimetry equation
q = CpmΔT
42
New cards
q
Heat energy (J - energy measured in joules)
43
New cards
Cp
Heat capacity (J/g*K)
44
New cards
ΔT
Change in temperature (K, C)
45
New cards
ΔH
change in enthalpy
46
New cards
Average Bond Enthalpy
The energy needed to break 1 mole of a bond of a gaseous molecule averaged over similar compounds
47
New cards
Stability in reactions
The products are more stable than the reactants, as they have a lower energy level, making it easier to maintain
48
New cards
Hess’s Law
The enthalpy change for a reaction that is carried out in a series of steps is equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps