CMS II Final: Rheum
1/208
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
which autoantibody (auto-ab) is commonly used for dx of lupus?
ANA
results are reported in titers: 1:80 is positive but >1:320 is strongly positive for autoimmune dz
which auto-ab is best for dx of RA?
Anti-CCP → may develop years before joint sx
what would the ESR estimate be for a 64 year old woman?
64/2 = 32 + 10 = 42
what are the 3 Cs for dx of septic arthritis?
cell count/diff
crystals
C&S plus NAATs (for chlamydia)
which dx has the classic triad of dermatitis, migratory polyarthritis, and tenosynovitis?
disseminated gonococcal infection
which joint is MC affected by disseminated gonococcal infection?
knee >>> hand + wrist >>> hip
rarely spine
what is the tx for uncomplicated gonococcal infection?
IM rocephin
tx partners!!!
what is the tx for disseminated gonococcal infection?
IV rocephin + doxy OR azithro (if NAAT positive)
tx partners!!
what is the first line tx for non-gonococcal arthritis?
vanco (bc MC staph aureus)
assoc. w IVDA
If a patient presents with bell's palsy and is found to have Lyme dz, how should you treat?
IV rocephin → neuro/cardio sx = always treat w IV
bell's = MC neuro sx
how many times should you give IV rocephin for Lyme?
NO MORE THAN 2X
what is the confirmatory test for Lyme?
western blot
after ELISA
pt presents with target-like rash that began 3 days ago after a hike. how should you treat?
lyme → doxy x3 weeks
erythro if preg
what is the primary regulator of extracellular calcium?
PTH → secreted in response to hypocalcemia
what is the action of PTH in the kidneys?
increased tubular resorption of calcium and stimulates kidneys to make activated form of Vit D
what is the active form of vitamin D?
1,25-(OH) vit D3
25 (OH) vit D2 = stored
where is calcium released from during a rapid response to hypocalcemia?
lacunar spaces
if the stimulus continues → osteoclasts resorb bone
what is the first line tx for osteoporosis?
Bisphosphonates → alendronate, risedronate, ibandronate, zoledronic acid
"-dronate"
which drug can cause irritation or burning of the esophagus?
bisphosphonates
also causes:
- abd/MSK pain
- osteonecrosis of jaw
- sub-trochanteric fx with >5 yr use
what is the most serious consequence of osteoporosis?
hip fx → often lead to death bc of comorbidities
vertebrae fx is MC
what are some risk factors for osteoporosis?
smoking and alcohol (esp in men)
there are others but she emphasized these
which SERM is approved for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis?
raloxifene → risk of DVT!
which type of osteoporosis is postmenopausal? Senile?
primary:
type 1 = postmenopausal (MC)
type 2 = senescence
which drugs are used to up-regulate osteoblasts and "build bone" in pts with osteoporosis?
anaBolics → teriparatide, abaloparatide, PTH, romosozumab
what is the black box warning for anabolics?
osteosarcoma
romosozumab specific = CV dz
what test is used to measure bone mineral density of the femoral neck to determine 10 year probability of fractures?
FRAX
which bones does a DEXA scan measure?
hips and lumbar (L1-L4)
gold standard for osteoporosis

what does a T score of -1 indicate? -2.5?
-1 = osteopenia
-2.5 = osteoporosis
is it okay to perform an arthrocentesis on an uncontrolled diabetic?
NO
dont do it in:
- overlying cellulitis, wound, bacteremia
- neuropathic joint
- coagulopathies
- prosthetics (...??)
- inaccessible joints (duh...?)
- lack of response previously
what dx is defined by compression of the neurovascular structures in the area just above the 1st rib and behind the clavicle?
thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS)
what is the MC facet of TOS?
brachial plexus (95%)
MCC by anomalous cervical rib
which dx shows 3 contiguous lumbar vertebra involved with NORMAL disc height?
DISH = ossification of the longitudinal ligaments of the spine that produce syndesmophytes
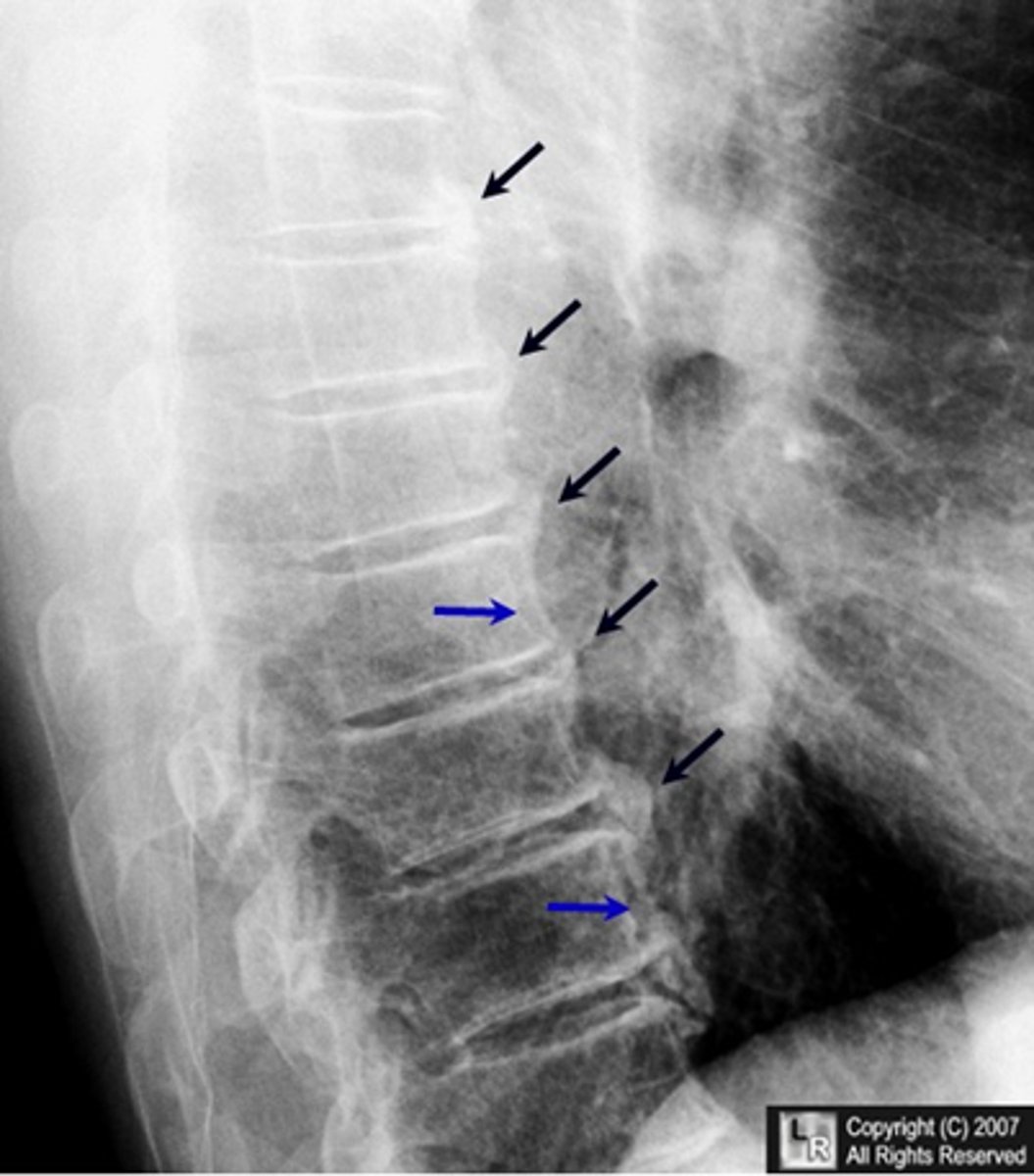
what comorbidities are often seen with DISH?
T2DM!!!!!
metaolic syndrome
also more common in men
what is the MC inflammatory dz of the axial skeleton?
ankylosing spondylitis
enthesopathy common
what is the hallmark of AS? Who is it seen in?
hallmark = upward migration of sacroilitis → get MRI
M>W; late teen/early 20s
what are the s/sx of AS?
iPAIN:
i = insidious onset
P = pain in PM/early AM
A = age <45
I = improves w exercise
N = no improvement w rest
what lab findings are assoc. with AS?
increased ESR/CRP
+ HLAB27 (DOES NOT always mean positive for AS)
bamboo spine = late finding

what is the first line tx for AS?
NSAIDs → Indocin
2nd line = TNF inhibitors
3rd = IL 12/23, IL-17
4th = JAK inhibitors
what is the first line tx for severe AS?
TNF inhibitors → adalimumab, certolizumab, etanercept, infliximab, golimumab
what happens if you use PO steroids for tx of psoriatic arthritis (PA)?
life-threatening rebound flare
what should you do if a male pt has new onset PA or reactive arthritis?
test for HIV
what are the subtypes of PA?
- asymmetric oligoarthritis with dactylitis (sausage fingers)
- DIP arthritis
- RA-like polyarthritis
- spondylitis
- arthritis mutilans
- HIV related

what s/sx are assoc with PA?
- generalized fatigue
- TTP, pain, swelling
- swollen fingers/toes
- stiff, pain, throbbing
- decreased ROM
- morning stiff/tired
- nail changes***
- conjunctivitis

which dx has the pencil in cup deformity?
PA

which dx has the triad of: conjunctivitis, urethritis, oligoarthritis?
reactive arthritis (Reiter's)
can't see can't pee can't climb a tree
which dx is assoc. with keratoderma blenorrhagicum and balanitis?
reactive arthritis

what is a common history finding for reactive arthritis?
hx traveler's diarrhea
reactive arthritis = autoimmune condition that develops in response to infection (GI or GU)
which dx is often seen in women who care for sick children, mothers, and daycare workers?
parvovirus B-19 → MC viral arthritis → "fifths" or "slapped cheeks"
IgM titers are _____ in acute parvovirus
HIGH
dx resolves in 2-4 weeks
in which dx may you see a transient generalized rash, small polyarticular joint swelling, and symmetrical pain?
parvo
what arthritis is often seen in IBD and GI pathology?
enteropathic arthritis → bowel related arthritis
what are risk factors for gout?
men >50
DM, HTN, HLD
thiazides
beer
fructose corn syrup

which dx shows up as yellow negatively birefringent, long, needle-like crystals?
gout → uric acid crystals
blue when perpendicular
why is gout more common in men?
estrogen is uricosuric
(so is high dose ASA)
which dx shows up as bite-like erosions on XR?
gout
which dx shows up as blue positively birefringent rod or rhomboid shaped crystals?
pseudogout (CPPD)
which dx is secondary CPPD associated with?
1. OA (MC)
2. hyperparathyroidism
3. hemochromatosis
4. hyperthyroidism
which dx shows chondrocalcinosis, subchondral cysts, and degenerative changes at 2nd/3rd MCPs?
CPPD
signs of OA BUT includes shoulders and MCPs which is uncommon in OA

what is the tx for osteomyelitis?
IV vanco x6 weeks
what is the best study for dx of osteomyelitis?
MRI
what is the order of tx for ACUTE gouty flares?
1. NSAIDs (Indocin)
2. colchicine
3. steroids
don't use NSAIDs in ppl with PUD
don't use steroids in DM
what is the order of treatment for chronic gout (>2 flares/yr, tophi, kidney stones)?
1. ULT (urate-lowering therapy) AKA Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (XOIs)→ allopurinol or febuoxstat
2. add uricosurics → probenecid, lesinurad
3. uricase agent
what is given for gout when ULTs are taking effect?
bridge of colchicine or NSAIDs x6 months to avoid flares
what is the target uric acid for chronic gout? what about tophaceous gout?
chronic = <6 mg/dl
tophaceous = <5 mg/dl
which drug is FDA indicated for chronic tophaceous and/or refractory gout?
Pegloticase (Krystexxa)(Savient)
what drug is recommended for chronic gout after failure with XOIs?
Lesinurad (Zurampic) → add to XOIs to get UA <6
what is the target for RA? OA?
RA = synovium
OA = cartilage
how many symptoms are needed for dx of RA?
4/7 x6 weeks (old criteria) --> now just need one large joint or 2+ small joints involved

where does RA affect most?
- C1-C2
- PIP
- MCP
- wrist
spares DIP, 1st CMC, and the rest of the spine

what is the gold standard for tx of RA?
methotrexate (MTX)
what is the #1 COD in RA pts?
ASCVD d/t proinflammatory state
what is the order of treatment for RA?
1. NSAIDs or MTX
2. MTX + TNF
3. MTX +Jak
what are the risks with TNF biologics?
increased risk for infection (esp TB), possible lymphoma/melanoma risk, drug induced lupus
boutonniere deformity and swan neck deformity are associated with ____
RA
what side effects are commonly seen with MTX?
nausea
LFT elevation
mouth sores
rash
diarrhea or loose stools
blood count abnormalities
lung probs
give folic acid!
which dx is associated with +ANA and uveitis in children <16?
juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA)
is hallux valgus or varus more common in RA?
valgus bc the lateral compartment is destroyed first
opposite for OA
what is the wink sign associated with?
RA d/t C1-C2 cord compression
look with open mouth XR view
TMJ = panorex
which type of synoviocyte phagocytoses cell debris and waste inside the joint cavity?
Type A
which type of synoviocyte provides nutrition to the joint?
Type B
what are the risk factors for OA?
- increasing age
- female
- obesity → MC in knee
- trauma/repetitive use
which joints are involved in OA?
- 1st CMC
- DIP (Heberden's nodes)
- PIP (Bouchard's nodes)
- knee
- hips
- lumbar spine
weight bearing joints
which joints are NOT involved in OA?
shoulder
elbow
wrist
foot
ankle
MCP
what is seen on XR in OA?
bony sclerosis, eburnation, osteophytes, loss of cartilage
do standing view bc weight bearing joints affected
which is MC in OA: Varus or valgus?
varus bc destruction starts medially
what is the 1st line tx for OA?
- TOPICAL NSAIDs → then oral
- 2nd line= other analgesics (tylenol)
NO SYSTEMIC STEROIDS EVER
what is the criteria for dx of fibromyalgia?
chronic widespread pain in all 4 quadrants → above and below the waist, left and right sides of body, and in the axial skeleton
>3 months
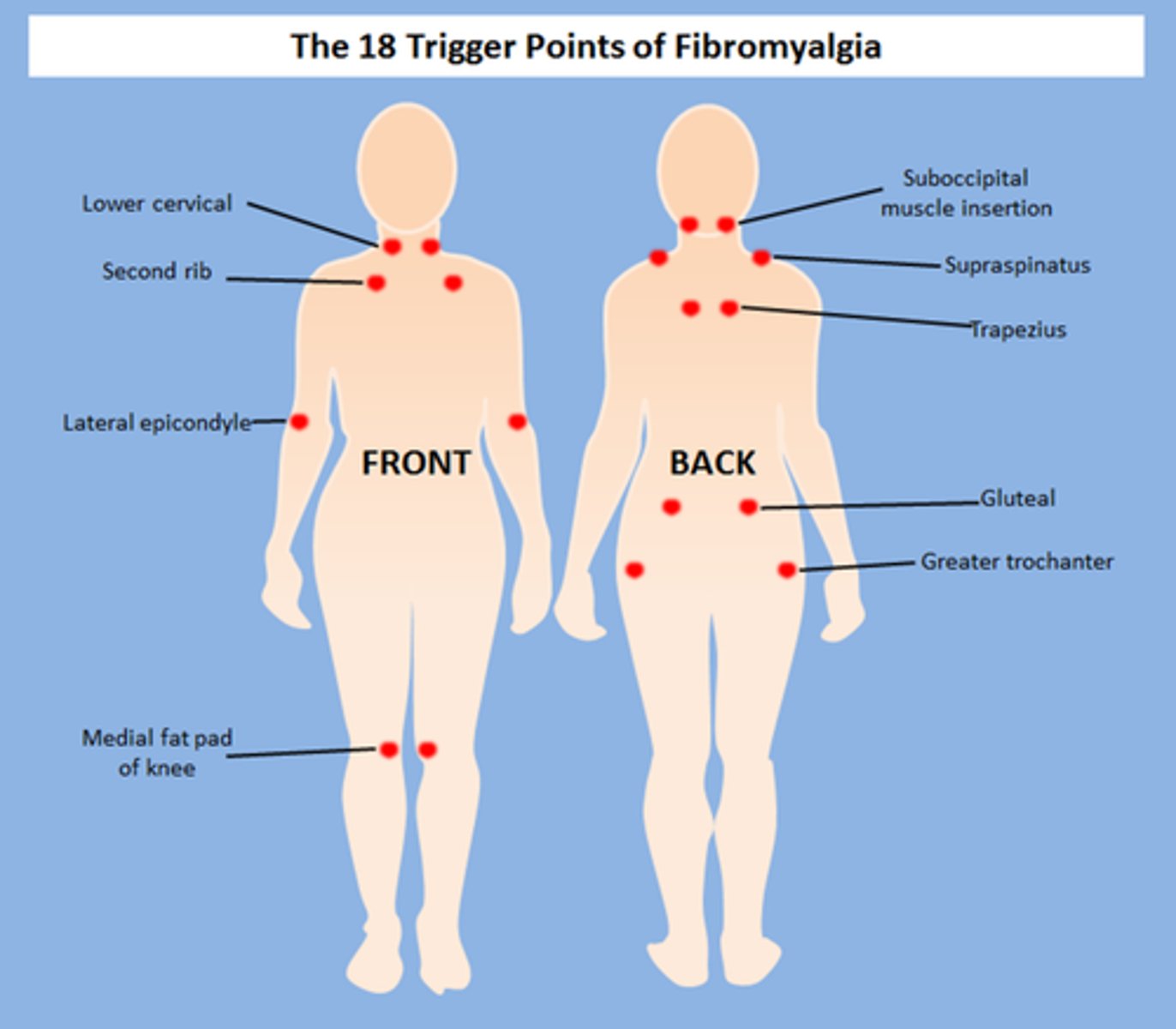
what is the 1st line tx for fibromyalgia?
1st = cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) (muscle relaxant)
NO PAIN MEDS/NSAIDs
what are the first 5 types of collagen?
1 = skin, tendon, bone*
2 = hyaline
3 = blood vessels, parenchymal cells
4 = basement membrane*
5 = smooth muscle
which type of extracellular macromolecule acts as a "multi-purpose glue" and binds extracellular components together?
proteoglycans
which type of extracellular macromolecules are adhesions molecules?
glycoproteins
which cartilage lines the joints?
hyaline
which type of cartilage is found in the C-spine and rib cage?
elastin
what is the enthesis?
connective tissue between tendon or ligament and bone
what are the first line treatments for CRPS in order?
1. analgesics/NSAIDs
2. antidepressants
3. anticonvulsants
who is CRPS common in?
W > M
younger age (<40)
upper extremity MC
follows minor trauma/surgery
which type of CRPS is d/t partial nerve injury?
type 2
type 1 is CNS afferent sympathetic rxn of joints/soft tissue
what is the best test to evaluate for CRPS?
bone scan → use Tc 99 mm
but radiography is initial study
which type of arthritis found in a young population MC affects the knee and is often monoarticular?
septic
knee>>>hand/wrist>>>hip
which dx is defined by abnormal bone remodeling?
Paget's
cardinal features = enlarged skull, tinnitus, bowed legs
