CMS III Final: Surgery
1/222
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
223 Terms
what is defined as removal or elimination of transient microorganisms from the skin and a reduction in resident flora?
antisepsis
what is the MC organism in wound infections?
staph aureus
what incision is on the right side of the abdomen for open exposure of GB and biliary tree?
kocher***

what is an agent that disinfects by destroying, neutralizing, or inhibiting the growth of disease-carrying microorganisms?
disinfectant
what is the state of being free from any living organisms?
sterility
what is the state of being free from disease-causing microorganisms achieved by sterilization and disinfection?
asepsis
what is a set of specific practices and procedures performed to make equipment and surfaces free from all microbes including spores by means of chemical/physical process?
sterilization
what is an agent that inhinits bacterial growth/reproduction?
bacterioSTATIC
what is an agent that kills/destroys bacteria?
bacteriCIDAL
which antiseptic solution is nonflammable but is contraindicated in iodine/shellfish allergies?
iodophor based (betadine) → slow release →prolonged activity but rapid onset!
okay to use in hairy areas!!**
which antiseptic solution has prolonged bactericidal activity x7 days but is flammable and should be avoided in areas with hair?
alcohol plus CHG (chloraprep)
what information should be obtained for surgery H&P?***
AMPLE
A - allergies
M - meds (+OTCs)
P - PMHx and PSHx
L - last meal(what and when)
E - events preceding emergency
which supplements inhibit clotting?
chamomile
dandelion root
how can you estimate post-op complications?
ACS NSQIP surgical risk calculator
how can you predict major cardiac events in adults undergoing non-cardiac surgery?
revised cardiac risk index (RCRI)***
what are the risk factors in the RCRI? (each is one point)
1. high-risk surgery
2. hx of ischemic HD
3. Hx of CHF
4. hx of CVD
5. preop tx with insulin***
6. preop creatinine >2
what is considered the sterile field on a surgical personnel?
above waist and below shoulder → anything that falls below level of pt table is contaminated

if a pt was planning on having elective non-cardiac surgery, but had to have drug-eluting stents placed, how long should surgery be delayed?
6 month to 1 yr***
if a pt was planning on having elective non-cardiac surgery but had to have bare metal stents placed, how long should surgery be delayed?
30 days
if a pt was planning on having elective non-cardiac surgery but had to have balloon angioplasty, how long should surgery be delayed?
14 days
which patients should receive abx prophylaxis to prevent infective endocarditis?
1. prosthetic cardiac valve/repair***
2. previous infective endocarditis
3. congenital HD (unrepaired, repaired within 6 months, or repaired with residual defects)
4. post-cardiac transplant valvulopathy
who should get an EKG and a TTE before non-emergent non-cardiac sx?
Fhx of genetic cardiomyopathy (<65 with no CV RF)
if a pt with insulin dependent DM is undergoing surgery, how should their insulin dose be adjusted?
decrease AM dose by half
how should you pass a team member in the OR?
front to front
or
back to back
what should be done for pts undergoing non-emergent non-cardiac surgery that is HIGH risk?
- < 65 without RF → EKG + biomarkers
- > 65 or CV RF → EKG + biomarkers + functional capacity assessment
- CV disease →EKG + biomarkers + functional capacity assessment + cardiac consult
at what platelet count is there a risk for spontaneous bleeding?
< 10-20k
what criteria is used to estimate peri op mortality in pts with liver pathologies?
Child Pugh Criteria
if a pt is on warfarin and clopidogrel***, how soon before surgery should they d/c?
5 days
if a pt is on ASA/NSAIDs chronically, how soon before surgery should they d/c?
1 week
if a pt is on rivaroxaban or apixaban (xarelto and eliquis), how soon before surgery should they d/c?
2-3 days
how would bridge therapy look in a person on warfarin?
5 days before → d/c wafarin***
3 days before ***→ start LMWH/unfractionated heparin
2 days before →check INR
24 hrs preop or 4-6 hrs preop → d/c LMWH
12-24 hrs POST op→ restart wafarin if stable
ASA classification***
ASA I- healthy patient
ASA II- mild systemic disease- no limitation
ASA III- severe syst. disease- definite limitation
ASA IV- severe syst. disease- constant threat to life
ASA V- moribund patient not expected to survive without surgery
ASA VI - brain dead

how soon before surgery should solid food be discontinued?
8 hrs
how soon before surgery should non-human milk be discontiued?
6 hrs
how soon before sx should breast milk be discontinued?
4 hrs***
how soon before sx should clear liquids be discontinued?
2 hrs
which surgical position facilitates access to perineum, groin, rectum, and inner thigh?
frog leg → hips and knees flexed and hips externally rotated
commonly used in uro/gyn sx

which surgical position facilitates venous return and improves exposure during abd/laparoscopic surgery? what are the disadvantages?
Trendelenburg → upward displacement of abd content into the diaphragm can decrease functional residual capacity thus requiring higher airway pressures to maintain ventilation
prolonged head down can increase ICP, swelling of face/larynx/tongue

which surgery position involves tilting the head of the bed upward such that the head is the highest point of the trunk?
reverse trendelenburg → facilitates upper abd surgery

in which surgery position is the patient lying supine with legs ABducted 30-45 degrees from midline with knees flexed?
lithotomy → commonly used during uro/gyn surgery***

which surgery position is used to access the thoracic cavity, retroperitoneum, or hip with the patient laying on non-op side with head in neutral position?
lateral decubitus
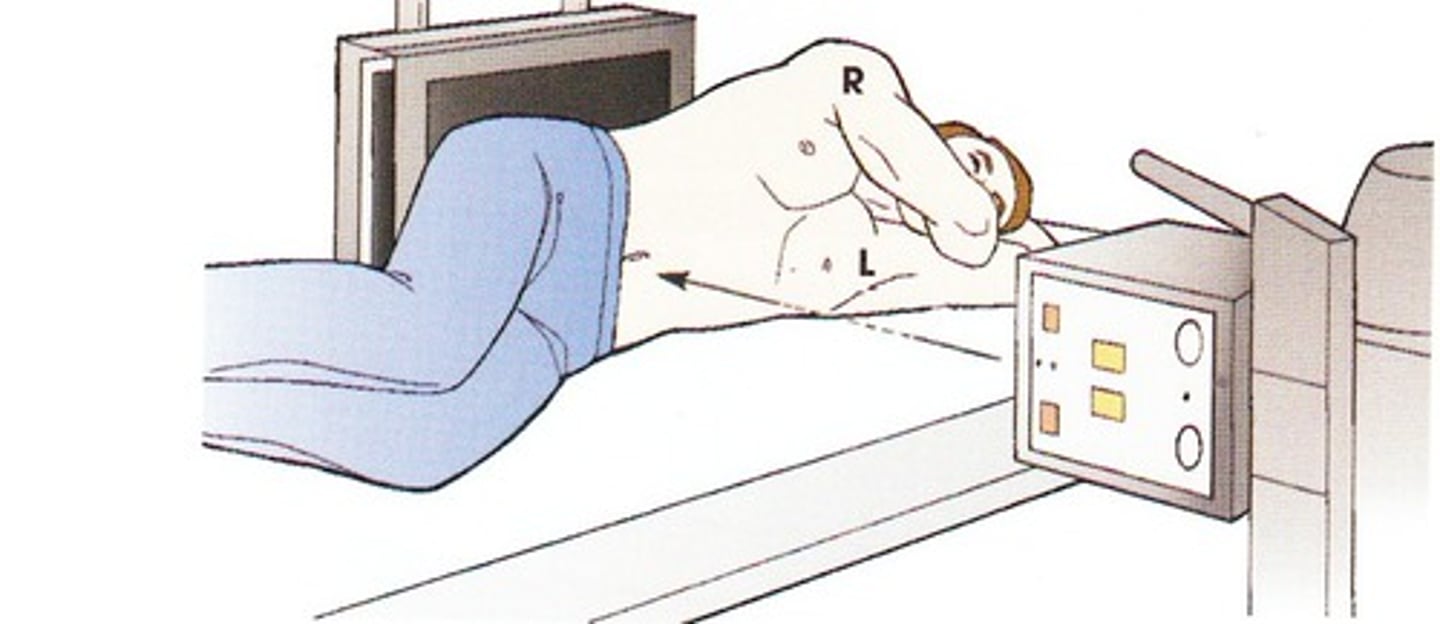
which surgery position is used during sx requiring access to posterior fossa, spine, butt, or perirectal area by having the pt lay face down?
prone → head, neck, spine in neutral position

which surgery position places the pt in prone with the head tilted down, hips flexed in knee-to-chest position?
jackknife→ used in colorectal sx

in which surgery position does the pt lay semi-prone on their L side with R knee and hip flexed and L knee and hip slightly extended?
Sims or Semi-prone → variation of LLD commonly used in anorectal sx

in which sugery position does the pt lay on their back with knees straight/slightly bent and head of the bed elevated between 45-60 degrees?
Fowlers → resp changes result in increased oxygenation by maximizing chest expansion and minimizing the effects of gravity on chest wall

what is the MC nerve injured from surgical positioning?
ulnar → from malposition of UE
how should surgical prep be performed?
start at the area of incision and move OUTWARD in circular motion***
clean → dirty

deficiency of which mineral can impair wound healing?
zinc***
when do pulm complications typically manifest post-op?
1-2 days
which anesthetic can suppress circulating cortisol?
propofol
which anesthetics inhibit cortisol production?
BZDs and opioids
when are pre-op abx given?
within 1 hr of surgery
which wound classification: clean, not infected, and no signs of inflam?***
class 1
which would classification: clean-contaminated?***
class 2 → low level of contamination
which wound classification: contaminated resulting from breach in sterile techniques or GI leakage?***
class 3
which wound classification: dirty or infected?***
class 4 → usually occur from inadequate tx of traumatic wounds, gross purulence, or evident infections
what is the goal core temperature during surgery?***
37 C
drop below 36 = hypothermia
what are the clinical features of malignant hyperthermia?
- rapid rise in body temp
- tachycardia
- tachypnea
- hypotension
- hypoxemia
- hypercarbia
- hyperkalemia
- met/resp acidosis
- cardiac dysrhythmias
- muscle rigidity
what is the gold standard for dx of malignant hyperthermia?
caffeine halothane contracture test --> don't use halogenated gases in pts with hx of malignant hyperthermia
what is the tx for malignant hyperthermia?
dantrolene***
what are the different types of GI tract tubes?
NG tube → start in nose and end in stomach
NJ tube → start in nose and end in jejunum
ND tube → starts in nose and ends in duodenum
Orogastric tube (OG) → starts in mouth and ends in stomach
Gastrostomy tubes (g tube) → placed thru skin straight into stomach
Jejunostomy tube (j tube) → placed thru skin straight into small intestine

which GI tract tube is preferred in pts at high risk for aspiration?
J tube
NG tube has most risk FOR aspiration***

who would require a stress dose of steroids pre-operatively?
pts on >20 mg of prednisone for >3 weeks within the last year
which lab value can indicate chronic malnutrition?
albumin!!!***
powerful predictors of post op pulm complications if <3
when are pts at highest risk for post op complications?
intermediate post op → increased susceptibility to nosocomial infections
how should you manage a pt with post op ileus?***
keep NPO --> NG tube if vomiting***
what is considered a post-op fever?
100.4
what are causes of acute (<1 week) post op fever?
killers → necrotizing infection, anastomotic leak, PE or MI
what are causes of subacute (1-4 wks) post op fever?
wound infection
UTI
PNA
C. diff
what are causes of delayed (>4 wks) post op fever?
endocarditis
infected implants
what are the Ws of causes of post op fever?
Wind → pulm (atelectasis, PNA)
Water → GU (UTI)
Walking → DVT/PE
Wound → SSI (anastomotic leak)
Wonder drugs → dx of exclusion (drug rxn, transfusion rxn)
what is the MC post op complication?
atelectasis → MCC of post op fever within 48 hrs of sx → encourage incentive spirometer***
what is the MCC of post op bleeding?
inadequate hemostasis → hemorrhage
most adults can lose 14-15% blood volume before symptomatic
which type of hemorrhage presents with unilateral weakness, HA, N/V, and AMS?
intracranial → get CT w/o contrast
which type of hemorrhage presents with hemothorax, chest pain, and SOB?
pleural cavity → get CXR, US, or CT
which type of hemorrhage presents with abd pain, hematemesis, hematuria, melena, and abd distention?
abdominal → FAST exam, CT, or abd XR
what are the contraindications for VTE anticoag?
active bleed
severe bleeding diathesis
immediate post op
severe trauma
acute intracranial bleed
when can dermabond (liquid adhesive) be used?
for lacerations in low stress areas

what is the preferred imaging modality for dx of intraabd abscess/peritonitis?
CT → tx with broad spectrum abx
which dx has sx of obstipation and intolerance of oral intake seen after abd sugery?
post-op ileus → d/t inflam of intestinal smooth muscle disrupting normal peristalsis
what are s/sx of post-op ileus?
diffuse abd pain/distention
N/V
inability to pass gas/BM
absent/diminished BS
abd tenderness
XR shows dilated loop of bowel
what is the MC etiology of post op wound infections?
S. aureus
what is included in a time out? when should it be done?***
1. confirm all ppl in room name and role
2. everyone confirm pt, site, procedure
3. verify abx given within 60 mins
done right before first incision
if a pt presents with erythema, edema, warmth, fever, and pain out of proportion 1-3 days following surgery, what is the likely dx?
necrotizing soft tissue infection
keloid or hypertrophic scar: grows beyond borders of original wound?
keloid → hypertrophic scars remain within original wound
which phase of wound healing is characterized by hemostasis, chemotaxis, and increased vascular permeability?
inflammatory phase (0-6) → platelets aggregate and activate clotting cascade; minimal wound strength
which phase of wound healing is characterized by formation of granulation tissue, re-epithelialization, and neovascularization?
proliferative phase (7-21) → tissue continuity is re-established, collagen synthesis, epithelial cell proliferation
which phase of wound healing is characterized by acellular collagen-rich scar formation and capillary regression?
maturation and remodeling (21+)
what are the factors of abnormal wound healing?
DIDNT HEAL
D - DM
I - infxn
D - drugs
N - nutrition
T - tissue necrosis
H - hypoxia
E - excessive tension
A - another concurrent wound
L - low temp
in which stage of anesthesia is the patient sedated but conversational?
stage 1 AKA analgesia/induction → ends when pt loses consciousness
in which stage of anesthesia does the pt experience delirium, uncontrolled movements, loss of blink reflex, HTN?
stage 2 AKA excitement/delirium → airway reflexes remain intact
in which stage of anesthesia do eye movements cease and pts have resp depression?
stage 3 AKA surgical anesthesia
which stage of anesthesia occurs when too much anesthesia has been given and results in severe brain/medullary depression?
stage 4 AKA overdose/medullary paralysis
which anesthetic is preferred when CV stability may be a concern?
etomidate→ risk of adrenocortical suppression; dont use in hx of epilepsy
which inhaled anesthetic should be avoided in pts with asthma d/t risk of laryngospasm?
desflurane → produces increased secretions
who should you avoid using competitive non-depol NMB in?
renal or hepatic dysfunction
-curonium
when is the initial and 2nd peak of transabdominal plane block (TAP)?
initial = 1 hr
2nd = 10-36 hrs
admin between transversus abdominus and internal oblique muscles
which local anesthetic has the longest duration of action?
bupivacaine ***→ good for nerve blocks
which local anesthetic has the fastest onset of action?
lidocaine (admin bicarb to reduce burning!!***)
when should contaminated areas be prepped?
LAST***