531 Med Chem Unit 1 Lec1-4
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
1
New cards
Sources of Drugs
•Natural extracts
•Natural products
•Synthetic drugs
•New drugs from existing drugs
•Screening synthetic chemical libraries
•Screening Natural product libraries
•Rational drug design
•Serendipity (chance)
•Natural products
•Synthetic drugs
•New drugs from existing drugs
•Screening synthetic chemical libraries
•Screening Natural product libraries
•Rational drug design
•Serendipity (chance)
2
New cards
What is screening corporate chemical libraries
Screen old chemicals for activity/targets
Ex: Prontosil (red dye)
Ex: Prontosil (red dye)
3
New cards
What is screening natural product collections
Ex: Screening plants from around the world→ Paclitaxel (anticancer drug)
4
New cards
What are natural products
pure molecules isolated from nature
\-Tend to be larger and more polar
\-Tend to be larger and more polar
5
New cards
Synthetic Drugs example & carbon source?
\-Carbon source is petroleum
Ex: Aspirin (acetylsalicyclic acid), chloral hydrate, chloroform, ether
Ex: Aspirin (acetylsalicyclic acid), chloral hydrate, chloroform, ether
6
New cards
New drugs from existing drugs examples
Ex: Antimalarial phenothiazine dyes, Chloropromazine (antipsychotic) to Imipramine (antidepressant)
7
New cards
Rational drug design Example
uses knowledge of drug target structure or enzyme mechanism to discover molecules that bind and modulate the activity of the target.
Ex: Pepsin & HIV
Ex: Pepsin & HIV
8
New cards
Serendipity drug example
Cisplatin (anticancer)
9
New cards
What are Important characteristics of a good drug
•Good oral bioavailability- water soluble but also small and lipophilic
•Chemically stable
•Chemically unreactive
•Metabolicallt stable- resistant to enzymatic breakdown in the body
•Pharmacologically specific- no off-target binding
•Potent but not too potent
•Good toxicity profile- wide therapeutic window
•Inexpensive to manufacture
•Chemically stable
•Chemically unreactive
•Metabolicallt stable- resistant to enzymatic breakdown in the body
•Pharmacologically specific- no off-target binding
•Potent but not too potent
•Good toxicity profile- wide therapeutic window
•Inexpensive to manufacture
10
New cards
Ionic Interactions
•Charge-Charge
•Often pH dependent
•Ions are solvated by water which competes with the interaction
•Often pH dependent
•Ions are solvated by water which competes with the interaction
11
New cards
Dipole & Dipole Induced Interactions
•Dipoles can be permanent or temp induced by a nearby charge

12
New cards
London Dispersion forces
•temporary attractive force that results when the electrons in two adjacent atoms occupy positions that make the atoms form temporary dipoles
•weakest intermolecular force
•bigger atoms have better LD
•Depends on polarizability
•weakest intermolecular force
•bigger atoms have better LD
•Depends on polarizability
13
New cards
Hydrogen bonding
•N, O and H
•Special case of dipole dipole interaction
•strongest when linear
•Donor- the one that has the H attached
•Acceptor- has partial negative charge
•Proteins use Hbonding to interact w polar groups and intramilecular Hbonding to fold
•Special case of dipole dipole interaction
•strongest when linear
•Donor- the one that has the H attached
•Acceptor- has partial negative charge
•Proteins use Hbonding to interact w polar groups and intramilecular Hbonding to fold
14
New cards
Example of Hbonding importance to drugs
Ex: antibiotic vancomycin kills gram positive bacteria by clamping down on D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of its peptidoglycan thanks to a Hbond from the Vancomycin to the amine of the D-Ala-D-Ala
\n Ester formation means no H bond and weak binding
\n Ester formation means no H bond and weak binding

15
New cards
Cation Pi Interactions
•Non covalent interaction between the face of an electron rich pi system (ex benzene) and a nearby hard metal cation or an ammonium cation
\
•The more negative the ring surface is the stronger the cation pi interaction
\
•The more negative the ring surface is the stronger the cation pi interaction

16
New cards
Desolvation and the Hydrophobic Effect
• Placing nonpolar molecules in water is energetically unfavorable because the surrounding water molecules are more restricted in motion reducing the entropy of the system
\
•hydrophobic drug can bind and free the water
\
**desolvation**: The removal of solvent from material in solution.
\
•hydrophobic drug can bind and free the water
\
**desolvation**: The removal of solvent from material in solution.
17
New cards
Higher log P means__ polar
Less polar
18
New cards
Lower log P means ___ polar
More polar
19
New cards
high pi (hydrophobicity scale)
Higher pi means more more hydrophobic
Lower pi means more hydrolphillic
Lower pi means more hydrolphillic
20
New cards
What is Log D
a pH dependent version of log P
\
At pH where the molecule is unionized logD=logP
\
At pH where the molecule is unionized logD=logP
21
New cards
How to estimate intrinsic binding energy
a summation of independent binding interactions
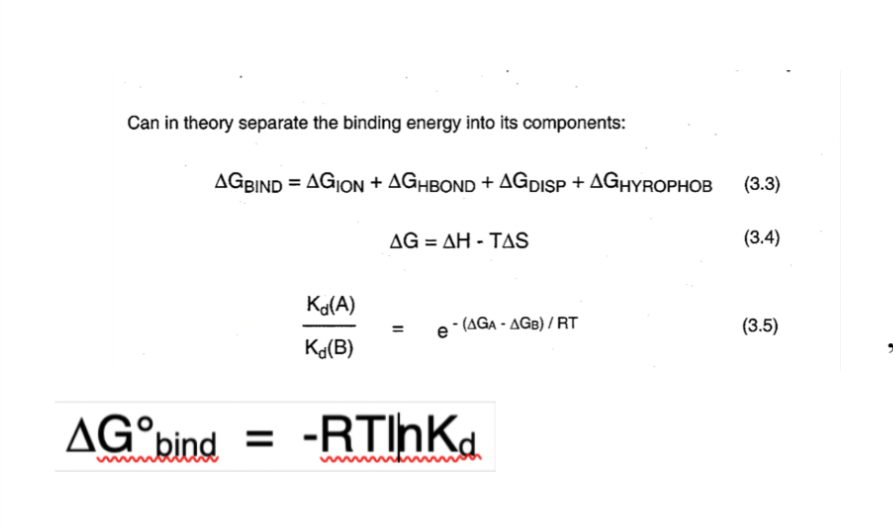
22
New cards
Cholinergic receptors
bind Acetylcholine
\-Metabotropic
\-Ionotropic
\-Metabotropic
\-Ionotropic
23
New cards
Metabotropic receptors
require G proteins and second messengers to indirectly modulate ionic activity in neurons
24
New cards
Ionotropic receptors
typically ligand-gated ion channels
25
New cards
Agonists
induce conformational change in their target receptor that triggers the signaling events
\
Mimics the full activity of the ligand
\
Mimics the full activity of the ligand

26
New cards
Antagonist
Blocks the effect of the liquid
27
New cards
Partial Agonist
Mimics the activity but plateaus at a lower level

28
New cards
Inverse Agonist
Has the opposite activity of the agonist
exerts opposite affect AND stops agonist affect
exerts opposite affect AND stops agonist affect
29
New cards
Effect
measure of biological output
→depends on binding but is a measurable action after binding takes place
→depends on binding but is a measurable action after binding takes place
30
New cards
Potency
measured along the x-axis by the ED50- the concentration of the ligand that gives 50% of its maximum effect
→ Less drug to get to 50% is more potent
→ Less drug to get to 50% is more potent
31
New cards
Methadone is a __
a full agonist of the mu opioid receptor
32
New cards
Buprenorphine is a___
More potent but only a partial agonist si is less “efficacious”
33
New cards
Naloxone is a …
competitive antagonist and blocks the effects of both agonists and partial agonists

34
New cards
Competitive Inhibition
shift the activity curve of an agonist to the right. It takes more agonist to give the full effect

35
New cards
Noncompetitive inhibition
Affect both binding and activity & prevent agonist from achieving full effect by binding at a different site on protein
\
Affects maximum output
Affects efficacy but not potency
\
Affects maximum output
Affects efficacy but not potency

36
New cards
Therapeutic Index
TD50 / ED 50 (human)
LD50 / ED50 (animal)
LD50 / ED50 (animal)
37
New cards
TD50
Median **dose** of a drug at which 50% subject show toxicity (people or cells)
38
New cards
LD50
**Dose** at which 50% of animals die
39
New cards
ED50
Dose of drug which shows 50% efficiacy for a population of subjects
40
New cards
Safe drugs have high or low TI ratios?
HIGH because you want only a high dose to be toxic and a low dose to be effective
\
TI= TD50/ED50
\
TI= TD50/ED50